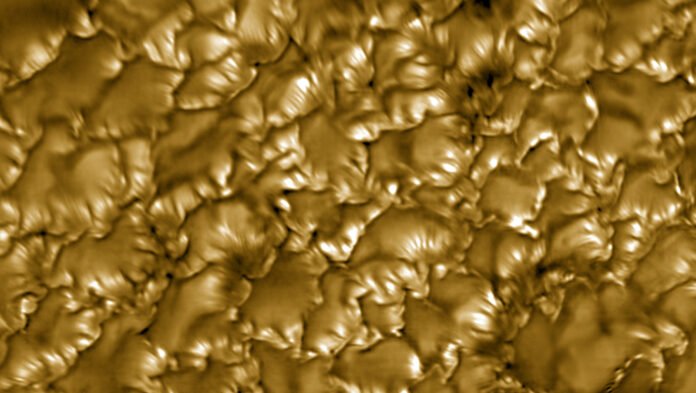
The National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope, located on the summit of Haleakalā on the island of Maui, Hawaii, captured the sharpest-ever images of the sun’s surface.
The images show ultra-fine bright and dark stripes (called striations) in the thin, gaseous layer of the sun’s atmosphere known as the photosphere, according to a statement from the National Solar Observatory (NSO), which operates the solar telescope.
“In this work, we investigate the fine-scale structure of the solar surface for the first time with an unprecedented spatial resolution of just about 20 kilometers [12.4 miles], or the length of Manhattan Island,” David Kuridze, lead author of the study and a NSO scientists, said in the statement. “These striations are the fingerprints of fine-scale magnetic field variations.”
The striations appear as alternating bright and dark stripes along the walls of solar granules — the convection cells that transport heat from the sun’s interior to its surface. These patterns result from curtain-like magnetic fields that ripple and shift like fabric fluttering in the wind.
As light from the hot granule walls passes through these magnetic “curtains,” variations in the magnetic field strength cause changes in brightness, effectively tracing the underlying magnetic structures. If the magnetic field is weaker than in its surroundings, it appears darker; if stronger, it glows brighter.
Therefore, the striations are believed to be signatures of subtle yet powerful magnetic fluctuations, which alter the density and opacity of the solar plasma. These slight shifts are only detectable thanks to the telescope’s Visible Broadband Imager (VBI), which operates in the G-band — a specific range of visible light that highlights areas with strong magnetic activity.
Unraveling the sun’s magnetic architecture is key to understanding phenomena like solar flares, eruptions and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which drive space weather and can impact Earth.
The team’s findings were published May 20 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.